In today’s digital age, email has become an essential communication tool for businesses and individuals alike. However, with the rise in spam and phishing attacks, email providers like Google and Yahoo have taken steps to protect their users by implementing stricter requirements for senders of bulk email. If you want to ensure that your emails reach their intended recipients’ inboxes and avoid being marked as spam or blocked, it’s crucial to understand and comply with these new requirements. In this article, we’ll explore the key changes introduced by Google and Yahoo and provide actionable tips to help you meet these requirements effectively.
Start by copying the Url below and adding your portal id with your browser
https://app.hubspot.com/settings/ADD YOUR PORTAL ID HERE/domains/
The Importance of Email Authentication
One of the primary requirements set by Google and Yahoo is the implementation of email authentication measures. Email authentication plays a crucial role in preventing threat actors from sending emails under the pretense of being from your organization, a tactic known as domain spoofing. To combat this, both Google and Yahoo require senders to have a combination of two authentication protocols in place: Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM).
SPF: Preventing Email Spoofing
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication protocol designed to prevent email spoofing, a common technique used in phishing attacks and email spam. SPF enables the receiving mail server to check whether incoming email comes from an IP address authorized by the domain’s administrator. By publishing an SPF record in your domain’s DNS settings, you can specify which IP addresses are allowed to send emails on behalf of your domain. This helps email providers like Google and Yahoo verify the authenticity of your emails.
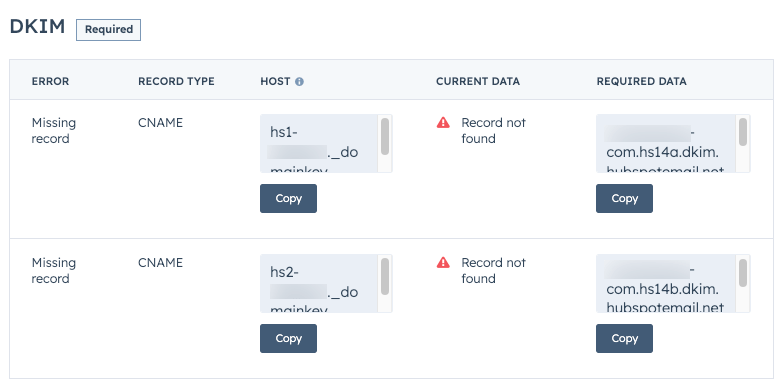
DKIM: Verifying Message Integrity
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is a protocol that allows an organization to take responsibility for transmitting a message by signing it in a way that mailbox providers can verify. DKIM record verification is made possible through cryptographic authentication. By adding a unique DKIM signature to your outgoing emails, you provide mailbox providers with a way to verify that the email originated from your domain and hasn’t been tampered with during transit.
Additional Requirements for Bulk Senders
If you send a large volume of emails to Gmail or Yahoo accounts, additional requirements apply to ensure a higher level of email security. These requirements are specifically aimed at bulk senders who send more than 5,000 emails per day.
DMARC: Domain-level Protection
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) is an email authentication standard that provides domain-level protection for the email channel. DMARC builds upon the existing standards of SPF and DKIM, allowing domain owners to publish a DMARC record in the Domain Name System (DNS). This record specifies the actions that receiving mail servers should take when an email fails authentication. By implementing DMARC, you can protect your domain against email spoofing techniques commonly used in phishing and business email compromise (BEC) attacks.
DMARC Alignment and Unsubscribe Options
To meet the requirements as a bulk sender, your emails must pass DMARC alignment checks. This means that the sending Envelope From domain should match the Header From domain, or the DKIM domain should match the Header From domain. By ensuring alignment, you provide mailbox providers with further assurance that your emails are legitimate and haven’t been modified in transit.
Additionally, Google and Yahoo require bulk senders to include a one-click unsubscribe option in all emails that require unsubscribe. This ensures that recipients have an easy and straightforward way to opt out of future communications. It’s important to honor unsubscribe requests promptly and within two days to maintain a positive sender reputation.
Meeting Google and Yahoo’s Requirements
Now that we’ve covered the key requirements set by Google and Yahoo, let’s explore how you can effectively meet these requirements and ensure the deliverability of your emails.
Step 1: Implement SPF and DKIM
The first step is to implement both SPF and DKIM authentication protocols for your domain. This involves updating your domain’s DNS settings to include the necessary SPF and DKIM records. Consult your domain registrar or IT department for guidance on how to add these records correctly. Once implemented, regularly monitor and maintain these records to ensure they remain up to date and aligned with your email sending practices.
HubSpot
Step 2: Set Up DMARC
To provide an additional layer of protection, set up DMARC for your domain. This involves publishing a DMARC record in your DNS settings, specifying the desired actions for receiving mail servers when an email fails authentication. You can choose either to monitor the email flow (p=none), quarantine suspicious emails (p=quarantine), or reject failed emails outright (p=reject). It’s important to note that implementing DMARC may require careful monitoring and adjustments to ensure legitimate emails are not mistakenly blocked.
Step 3: Monitor and Maintain Reputation
Maintaining a positive sender reputation is crucial for email deliverability. Regularly monitor your email sending practices and ensure compliance with Google and Yahoo’s guidelines. This includes monitoring spam rates reported in Google Postmaster Tools or mxtoolbox.com, aiming to keep them below the recommended thresholds. Additionally, implement best practices such as sending emails in the correct format (RFC5322 compliant) and avoiding any activity that may impersonate Gmail’s From: headers.
Step 4: Provide Easy Unsubscribe Options
As a bulk sender, it’s essential to provide recipients with an easy and one-click unsubscribe option. Include List-Unsubscribe message headers and a clearly visible unsubscribe link in the email body. Promptly process unsubscribe requests and remove unsubscribed recipients from your mailing lists within two days. By respecting recipients’ preferences, you not only comply with Google and Yahoo’s requirements but also promote a positive email sending reputation.
The Risks of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with Google and Yahoo’s requirements can have severe consequences for your email deliverability and sender reputation. Emails that don’t meet the authentication and alignment criteria may be marked as spam or blocked entirely, resulting in undelivered messages and missed business opportunities. Additionally, a poor sender reputation can have long-lasting effects on your domain’s credibility and trustworthiness.
To avoid these risks, it’s crucial to prioritize email authentication and comply with the requirements set by Google and Yahoo. By implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, monitoring your reputation, and providing easy unsubscribe options, you can ensure the deliverability of your emails and maintain a positive sender reputation.
In an era of increased email threats and evolving cybersecurity measures, it’s essential for businesses and individuals to adapt and comply with email authentication requirements. Google and Yahoo’s stricter requirements for senders of bulk email aim to protect users’ inboxes from spam and phishing attacks. By implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, monitoring your reputation, and providing easy unsubscribe options, you can ensure your emails reach their intended recipients and maintain a positive sender reputation. Stay proactive, stay compliant, and keep your email communications secure and effective.